A radiant smile not only exudes confidence but also relies on a strong foundation. When it comes to dental implants, a crucial consideration is the density and health of the jawbone. In cases where bone volume is insufficient, bone grafting emerges as a transformative solution. Let’s delve into the intricacies of bone grafting for dental implants, unraveling the key aspects that contribute to a solid and enduring smile.
The Foundation of Dental Implants: The Importance of Jawbone Health
The success of dental implants hinges on the integrity of the jawbone. An ample and sturdy foundation is essential for the secure integration of implants, ensuring stability and longevity. However, various factors, such as tooth loss, gum disease, or natural bone resorption, can lead to diminished bone volume.
Enter Bone Grafting: A Restorative Marvel
**1. Understanding Bone Grafting:
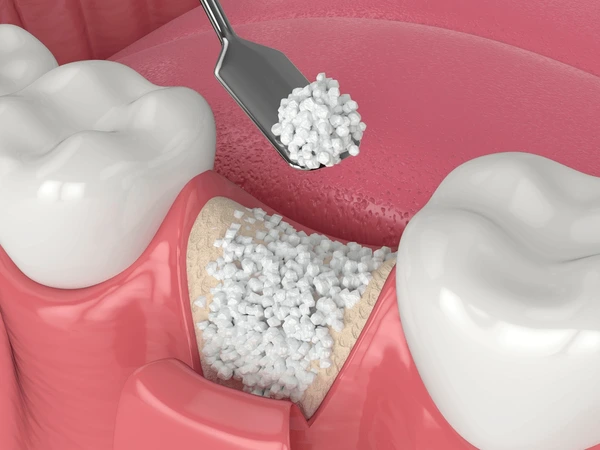
- Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that involves augmenting or rebuilding areas of insufficient bone. The graft, often sourced from the patient or a donor, serves as a scaffold, promoting the growth of new bone tissue.
**2. Types of Bone Grafts:
- Different types of bone grafts exist, including autografts (from the patient’s own body), allografts (from a donor), xenografts (from animals), and synthetic grafts. Each type is chosen based on individual needs and circumstances.
**3. The Bone Grafting Process:
- The procedure typically begins with a comprehensive examination, including imaging to assess bone volume accurately. During the surgery, the graft material is strategically placed in the deficient areas, encouraging the body’s natural ability to regenerate bone.
**4. Healing and Integration:
- Post-surgery, a healing period ensues. The grafted material fuses with the existing bone through a process called osseointegration. This integration is crucial for creating a robust foundation capable of supporting dental implants.
When is Bone Grafting Necessary?
**1. Tooth Extractions:
- After a tooth extraction, bone grafting may be recommended to preserve the socket and prevent bone loss.
**2. Sinus Lifts:
- In the upper jaw, bone density near the sinuses can be insufficient. A sinus lift involves elevating the sinus floor and grafting bone to enhance the implant’s stability.
**3. Periodontal Disease:
- Advanced gum disease can erode the supporting bone. Grafting restores lost bone, creating a suitable environment for implant placement.
**4. Trauma or Injuries:
- Facial injuries or trauma may result in bone loss. Grafting repairs and regenerates the damaged areas, preparing the site for implants.
Benefits and Considerations:
**1. Enhanced Implant Success:
- Bone grafting significantly improves the success rate of dental implants by ensuring a solid foundation for implant integration.
**2. Improved Aesthetics and Functionality:
- Grafting enhances the overall aesthetics of the smile and restores proper functionality by addressing bone deficiencies.
**3. Long-Term Stability:
- A well-executed bone graft lays the groundwork for stable, long-lasting dental implants, promoting oral health for years to come.
Conclusion: A Solid Foundation for a Lasting Smile
In the realm of dental implants, bone grafting stands as a transformative procedure, revitalizing smiles and ensuring the durability of restorative efforts. By addressing inadequate bone volume, this process lays the groundwork for a smile that not only radiates confidence but is also built to last. If you’re considering dental implants and bone grafting, consult with a qualified dental professional to explore how this restorative marvel can elevate your oral health.


